PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
UN NO.
TOXICITY
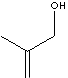
SMILES
C(CO)(C)=C
CLASSIFICATION
Acyclic, Alkene
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
320 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
33 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://www.faqs.org/
The polyalkylene glycol monomer of the present invention has a polymerizable
double bond and a polyalkylene glycol chain having a hydrophobic part in the
chain and/or at a terminal of the chain, and includes the following monomers
and. The polyalkylene glycol monomer, wherein the polymerizable double
bond is derived from allyl glycidyl ether (hereinafter, also referred to as
polyalkylene glycol monomer and the polyalkylene glycol monomer,
wherein the polymerizable double bond is derived from isoprenol, allyl alcohol,
or methallyl alcohol, and the hydrophobic part is derived from glycidyl ether
containing 1 to 20 carbon atoms (hereinafter, also referred to as polyalkylene
glycol monomer (b). The term "polyalkylene glycol monomer" means both of the
polyalkylene glycol monomer (a) and the polyalkylene glycol monomer
Local: Allyl alcohol is a clear liquid, boiling at 96 C; soluble in water. It is highly toxic and hazardous to the environment. It requires special attention to handling procedures. It is made by the hydrolysis of allyl chloride or isomerization of propylene oxide. It is used as a starting material in making various polymers, pharmaceuticals, pesticides and other allyl compounds. Allyl- is the prefix for the univalent organic group, -CH2=CHCH2. Allyl alcohol is an example, CH2=CHCH2OH, clear, pungent liquid, boiling at 96 C; soluble in water. It is prepared from allyl chloride by hydrolysis. Allyl compound, an alkene hydrocarbon, has a vinyl group, CH2=CH-, attached to a methylene -CH2. Because of the highly reactive solid bond, allyl can undergo free radical addition to solid bond which readily combine with themselves or other monomers to form homopolymers or co-polymers which are used in the production of coatings, adhesives and elastomers. In addition to free radical addition, allyl compounds can participate in a wide variety of reactions including electrophilic additions, allylic substitution and oxidation. Allyl, an unsaturated bond, imparts a characteristic odor in some compounds. An example is allyl isothiocyanate which is the main ingredient of black mustards. (white mustard consists principally of p-hydroxybenzyl isothiocyanate). Allyl isothiocyanate is called mustard oil. Allyl esters are involved in fragrance, flavor, or odor.
Methallyl alcohol is a clear liquid boiling at 115 C. It is flammable and toxic clear liquid soluble in most organic solvents. It is used as a starting material in making various polymers, pharmaceuticals, pesticides and other allyl compounds.
APPEARANCE
PURITY
98.5% min